Deep Dive into Customer Journey Maps: How to Analyze eCommerce Customer Behavior?

Do you want customers to return more often, stop abandoning their carts, and recommend your online store to their friends? Then, you need to find out how they use your eCommerce app (web or mobile) and what motivates them to do so.
A customer journey map allows you to analyze how users navigate the app and determine what changes could improve their experience. As a result, it helps you increase the number of conversions.
Learn how to prepare a customer journey map and improve your eCommerce app development strategy.
What are customer journey maps in the context of eCommerce?
Customer journey maps (or user journey maps) visualize, step by step, the actions a persona takes in a mobile or web app (a website).
Sometimes, these maps also include the stage preceding the moment when the user opens the eCommerce app.
For example, when users realize they cannot complete a task without a particular product, they need to find a store where they can buy it. This approach allows for a better understanding of customer needs and their challenges.
Why create and analyze customer journey maps?
The benefits of creating customer journey maps may vary depending on the project stage, the problems you want to solve, and your business goals.
Product Discovery stage: Creating a product vision
This is the initial stage of the project when we collect information about the target group and competitors and establish business goals. It allows us to refine the product vision, i.e., the eCommerce app (mobile or web).
Often, at this stage, UX workshops are held, during which we analyze the collected information, generate ideas for solutions, and check the project from a technical point of view.
What are the benefits of creating a customer journey map at this stage?
- A better understanding of customer motivations and needs – when mapping the user journey, we rely on data and information from store employees who work with customers (e.g., customer service agents). Thanks to this, our customer shopping path accurately reflects user behavior and is not based on guesswork. It allows us to better understand why they take certain actions or decisions.
- Generating ideas for solutions tailored to customer needs – when we know what users need, we can work on new solutions enabling them to achieve their goals that are perceived as valuable.
- Designing solutions that build positive customer experiences (CX) – customer journey mapping allows you to identify which moments in the journey can cause frustration. Thanks to this, you can devise solutions in advance that eliminate them or provide positive experiences.
Continuous Discovery stage: Development of an existing mobile or web app
This stage occurs when you already have a functioning web or mobile app and want to change it.
We also recommend conducting research and organizing Continuous Discovery workshops during this project phase.
Why should you consider a customer journey map in the Continuous Discovery phase?
- Identifying what factors trigger negative emotions in customers and lead to undesirable actions (such as abandoning a cart or refusing to create an account) – the map shows the customer’s actions and the emotions accompanying them. It allows you to notice which stages of the path negatively affect CX and contribute to a decrease in conversion.
- Improved usability of the app/website – the customer journey map allows you to adopt a User Centered Design (UCD) approach, which assumes that the design is primarily guided by the user, their needs, and desires. Thanks to this, the eCommerce app can be more intuitive and better meet customer expectations.
- Increased conversion – the ultimate business goal is usually to increase sales, and user journey mapping brings you closer to it because it allows you to better tailor solutions to the target group’s needs and focus on those elements of the user journey that really require changes.
- Increased number of loyal customers – creating user journey maps is a step towards designing a better CX, and a satisfied customer is more likely to return to the store and recommend it to others, which in turn also allows you to reduce marketing expenses.
User journey mapping step by step
What does creating customer journey maps look like? This process consists of several stages.
1. Determining the purpose of the analysis
If the user journey map is to help you create solutions that will translate into measurable success for your store, you need to determine exactly what goal you want to achieve with such an analysis. Why?
First, it will mobilize your team to act – the vision of specific benefits makes people involved in the project more willing to take the initiative, leading to better results.
Secondly, setting goals will indicate which aspects of the customer journey map to focus on.
Last but not least, it will allow you to determine what data sources and expertise you will need to create a map.
Example
Let’s say you run an online store that sells sportswear through a web app (i.e., a website). For some time now, you have been noticing a decrease in the number of transactions. The average basket value and the number of returning customers are also getting lower.
With your team, you prepare a customer journey map to determine what may be causing the observed problems and develop solutions that will encourage customers to shop more often.
2. Collecting data
In case of user journey maps, the results depend on various data about user behavior in the app that you’re able to collect. It allows you to analyze the user experience.
The McKinsey & Company article indicates that organizations that use customer behavior insights outperform the competition by 85% in terms of sales growth.
To get the most complete picture, use quantitative and qualitative data.
Quantitative data
This type of data informs about what users are doing and what is happening in the market.
Examples of sources of quantitative data:
- Surveys
- Reports from analytical tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Hotjar, etc.)
- A/B testing reports
- Reports on eCommerce and statistics related to your industry (e.g., European E-Commerce Report 2024, eCommerce in Europe 2024, Statista).
Tip: You can use AI tools to analyze materials and create summaries. It will save you time, and you’ll be able to find the information you need for user journey mapping quickly.
 Qualitative data
Qualitative data
This data explains why customers take certain actions.
Examples of sources of qualitative data:
- Interviews with customers or potential customers
- Interviews with customer service representatives
- Usability testing

What else might be useful? Consider what sources of information you have access to and what materials other departments in your company use.
For example, marketing may base its work on personas representing the main target groups, and HR may have onboarding materials for new employees, where cases that often occur with customers are described.
3. Choice of tools
You have collected all the information? Great, now, choose a tool for user journey mapping. If your team works remotely, choose a solution that enables online collaboration, such as FigJam, Miro, or Mural. This will allow everyone to make changes, share their comments, and actively participate in preparing the map.
4. Data analysis
Before you start customer journey mapping, analyze the collected data. Select the most important information that may be useful for the task and transfer it to an online board or flip chart. You can group them thematically and use the affinity mapping method for this:

At this stage, the Google NotebookML tool may be helpful. It will summarize the key takeaways from documents and indicate answers to questions about user behaviors described in the provided materials.
5. Visualization of paths
Finally, you get to work on the customer journey map. Where should you start?
First, prepare a user journey map template that you will fill out with customer information. You can choose a ready-to-use solution offered, for example, by Figma or Miro. Just think about the goals you set in the first step and check if the template contains all the fields you are interested in.
What fields are worth including in the user journey map?
- Customer journey stage
- Quote
- Context
- Description of activities
- Emotions (negative, positive, neutral)
- Comments/ideas for solutions
Then, select the persona you want to focus on in this task. You want to solve their problems with the map.
After that, with your team, fill in the information assigned to individual stages – from the moment the user realizes the problem through searching for a solution to finding and solving it.
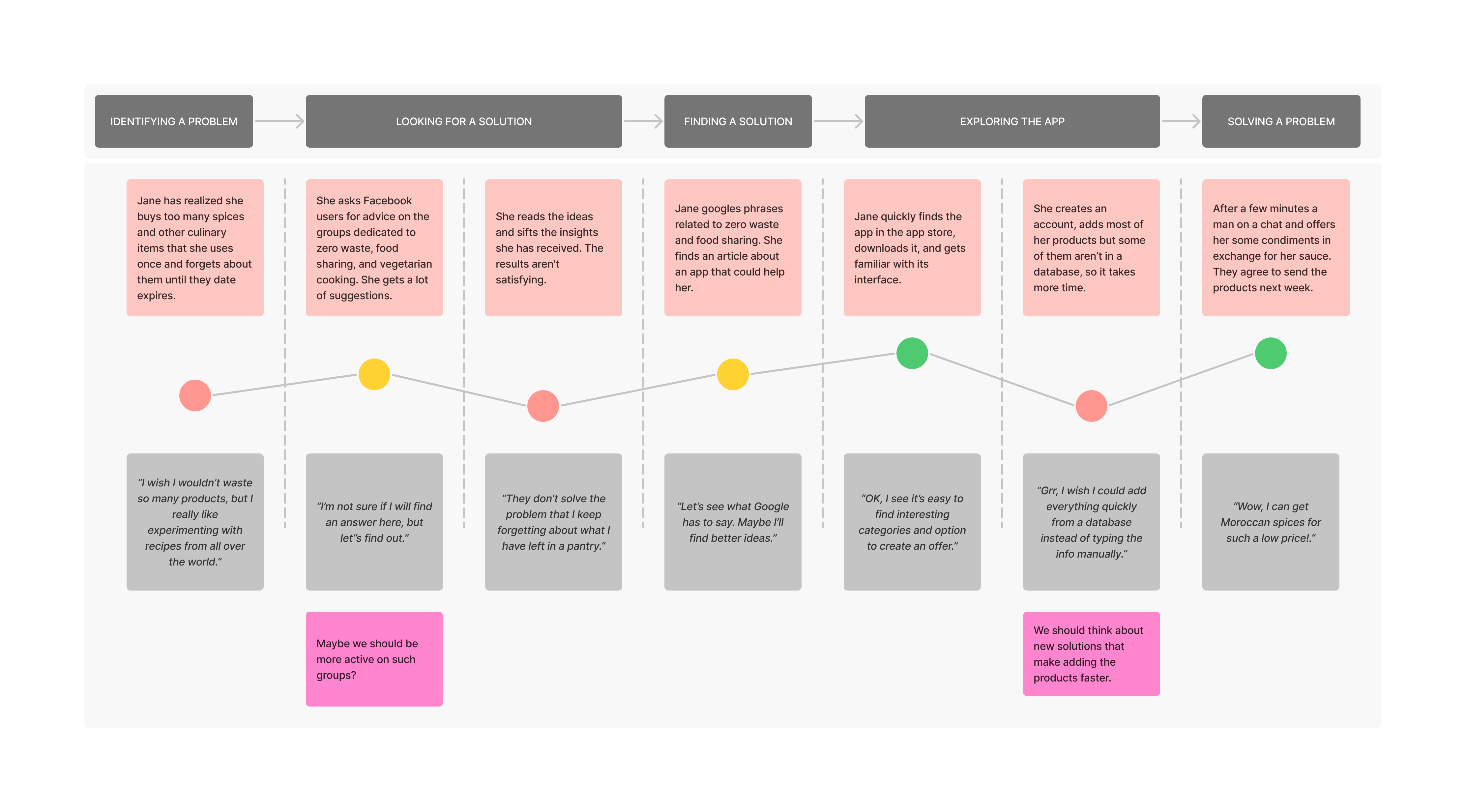
Example
Let’s say you have an eCommerce web app and sell construction tools.
- [Awareness of the problem] Anna is planning a renovation and realizes that she will not be able to hang the picture without a drill, so she decides to buy it online.
- [Searching for a solution] Anna types the phrase “cheap drills” into the search engine and clicks on the ad that appears.
- [Finding a solution] Anna reads the drill parameters, learns how to use the tool, and decides to buy it.
- [Finding a solution] Anna orders the product with immediate delivery.
- [Solving a problem]Anna receives the product, makes sure it is consistent with the description, and tries it out right away.
This is, of course, a very shortened customer journey. You can add, for example, user quotes from interviews or surveys to each activity, information about the persona’s mood at a given moment, etc. Be sure to include accurate descriptions of interactions with your store’s app where relevant.
Such a path breakdown will allow you to notice user pain points – moments when they have negative experiences related to using the store’s app.
Your next task is to introduce solutions that will improve them, thus increasing customer satisfaction and contributing to conversion growth.
6. Data interpretation and proposing solutions
After determining which touchpoints with your online store cause negative emotions, brainstorm solutions with your team. Take the user’s perspective and consider what could make their experience positive or at least neutral. Think about how you can eliminate the problems they encounter along the way.
Let each team member propose their solutions. Together, you can analyze them and choose the ones that you think are the most promising.
Tip: At this stage, competitor analysis is useful. The solutions of other stores can inspire you when devising your own features that will lead to improved customer experiences.
Examples of critical points:
- The user cannot find all the product information, which annoys them and makes them leave the store’s website.
- The customer loses patience when filling out the registration form, where many details are required, and it is not always clear why. They feel frustrated and lose the desire to create an account.
- The UX design suggests that the shopping cart view is displayed, but it is actually the order summary view. The customer does not understand why they cannot increase the quantity and does not know how to return to the previous view.
Solutions:
- Reviewing and simplifying the form and explaining why some information is required.
- Adding detailed product descriptions, photos, and videos.
- Improving the UX/UI design, including changes to navigation and nomenclature on the site, will facilitate the use of the app.
The customer journey map is ready – what’s next?
In the next step, summarize the collected ideas, highlight the highest-priority solutions, and pass them on to the software developers for technical analysis. Their task will be determining if their implementation is possible and, if so, how difficult and time-consuming it may be. They can also recommend alternative solutions.
And what about the situation when you are unsure if the idea is good? Then, it is worth considering A/B tests. In these tests, different customer groups see different versions of an app element – one group sees the current version, and the other sees a new one.
Remember that the customer journey map needs to be updated regularly—UX design trends, customer behaviors, and preferences change. In addition, technical problems may arise. Up-to-date customer journey maps will allow you to react quickly in such cases.
Customer journey maps for your store: a summary
Start creating and analyzing user journeys to offer customers better experiences and, as a result, increase their loyalty. Customer journey maps help improve the UX of online stores. They also help devise solutions to build better relationships with users, leading to more frequent purchases.
You’re not sure how to prepare your own user journey map? Or perhaps you lack specialists who have knowledge in UX design and mobile or web app development? Contact us and schedule a workshop. Our team will be happy to help you analyze data and develop new solutions.






